-
tel:
+86-15371113672 -
WhatsApp:
+86-15371113672 -
email:
qianli@jsryan.com
What Makes a Non-Standard Custom Electric Thermal Oil Heater Different from Standard Models?
News List
- Petroleum and Gas
- How Do You Maintain and Service Non-Standard Custom Electric Thermal Oil Heaters?
- Are Electric Process Air Heaters Energy-Efficient?
- What Safety Features Should in a Non-Standard Custom Electric Thermal Oil Heater?
- What Are the Key Advantages of Using Electric Air Heaters Over Traditional Heating Methods?
- What Are the Benefits of Using Thermal Oil as a Heat Transfer Medium?
- How Does an Electric Process Air Heater Work?
- What Makes a Non-Standard Custom Electric Thermal Oil Heater Different from Standard Models?
- What Industries Benefit from Electric Process Air Heaters?
- Client feedback of Vacuum pyrolysis oven and preheat oven
- Suggestions for selecting electric thermal oil heater
- How to install and use the electric thermal oil heater
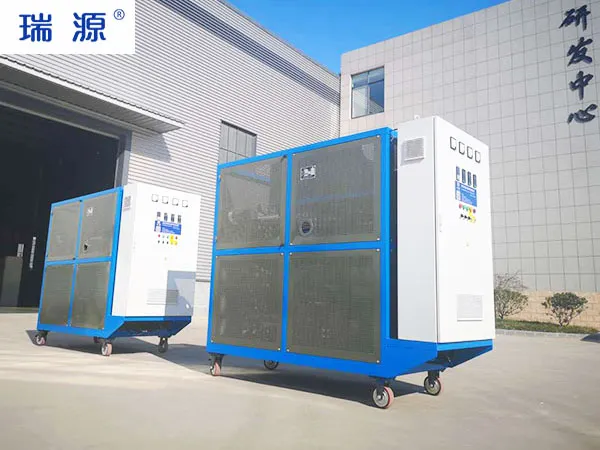
- Deliver five sets of explosion-proof organic fluid boiler with cool unit
08 Jun
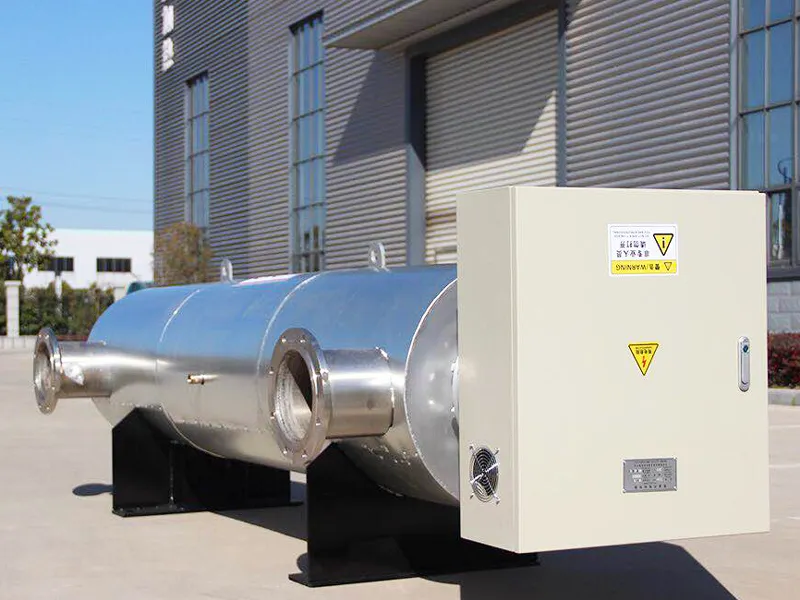
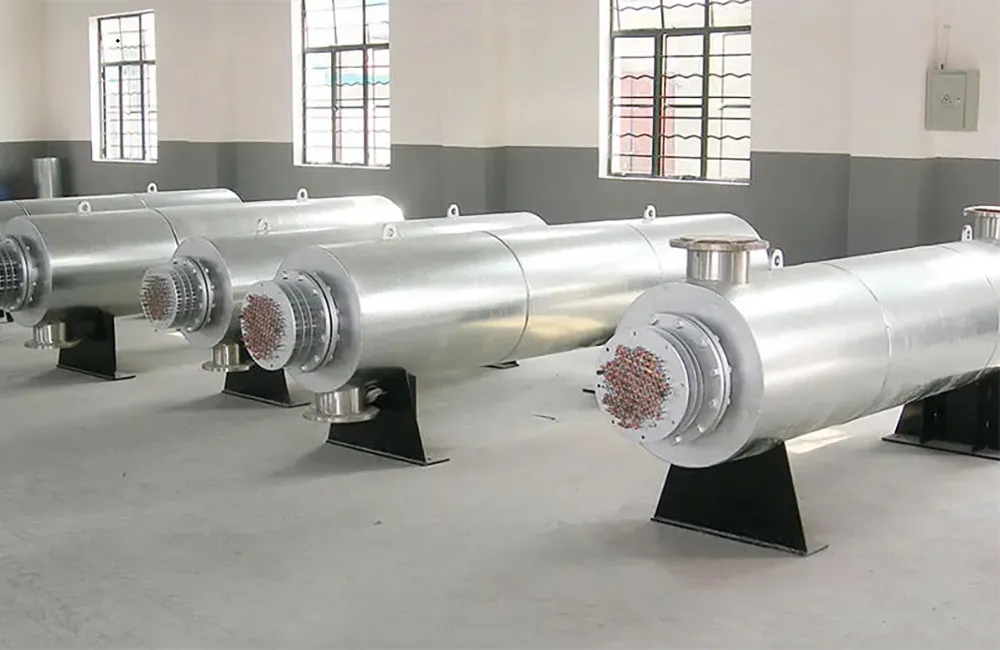
Electric thermal oil heaters are critical components in many industrial heating applications. They provide efficient and controlled heat transfer using thermal oil as a medium. While standard models work well for general applications, non-standard custom electric thermal oil heaters are designed to meet unique operational challenges and specialized process requirements.
So, what sets a non-standard custom heater apart from its standard counterpart? The differences span several key areas: design flexibility, materials, control systems, performance specifications, integration capabilities, and compliance with industry-specific standards. Let’s break it down.
1. Customized to Specific Process Requirements
A standard thermal oil heater typically comes in a fixed set of configurations. These include a predefined power rating, temperature range (usually up to 350°C), and basic control features. While sufficient for many uses, such designs may not meet the unique requirements of certain industries or processes.
In contrast, non-standard custom heaters are engineered based on the customer's specific needs, including:
Desired temperature range (which may exceed standard maximums)
Required heat transfer rate (kW or BTU/hr)
Flow rate and pressure compatibility with existing systems
Integration into space-constrained or unusual plant layouts
Fluid properties such as high viscosity, corrosiveness, or flammability
This level of customization ensures higher efficiency, safety, and longevity under conditions that would strain or limit a standard unit.
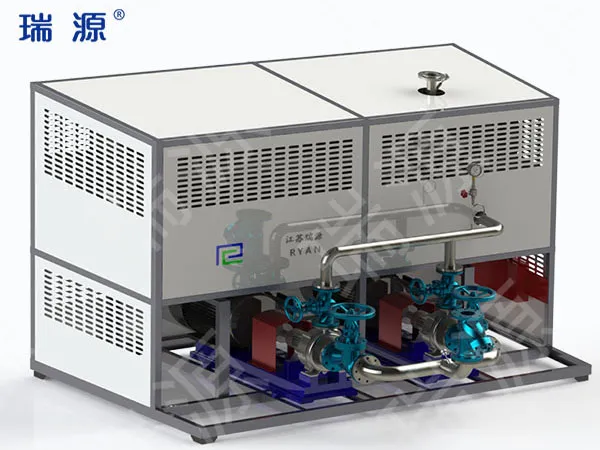
2. Flexible Configurations and Mounting Options
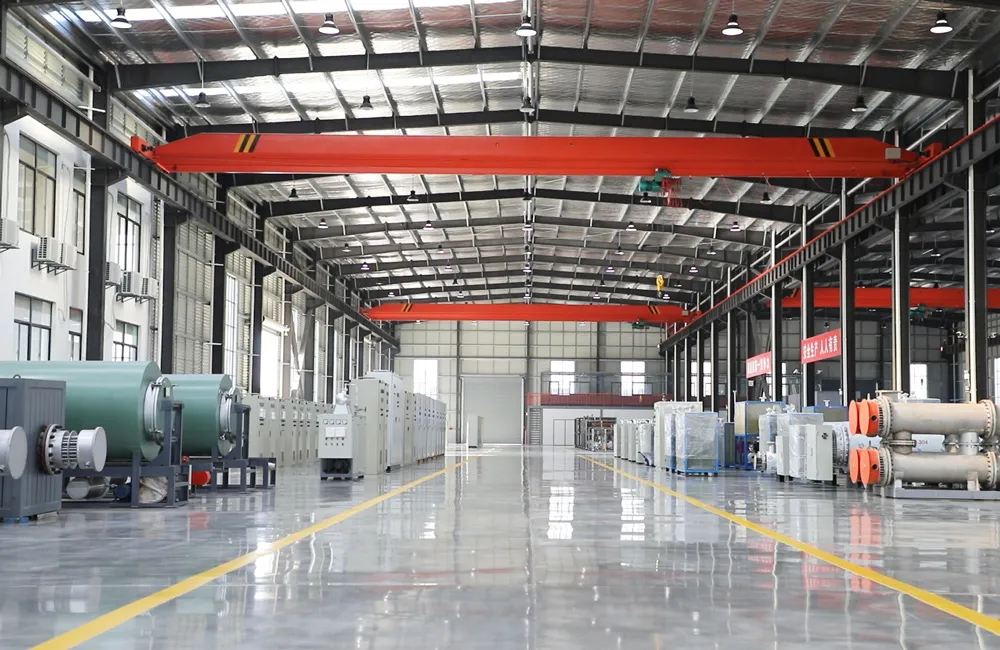
Standard heaters are typically built for general-purpose mounting—horizontal or vertical floor-standing models. However, custom electric thermal oil heaters can be tailored to any footprint, enabling installation in tight, awkward, or mobile settings.
For example:
Skid-mounted systems that include the heater, expansion tank, circulation pump, and control panel on a single platform for plug-and-play deployment
Wall-mounted or rack-mounted units for compact manufacturing environments
Mobile units on trolleys or in enclosures for field or remote site applications
Split systems where the heating elements, control panel, and oil circulation components are separated to fit existing infrastructure
This design flexibility allows custom heaters to meet complex system integration needs without compromising functionality.
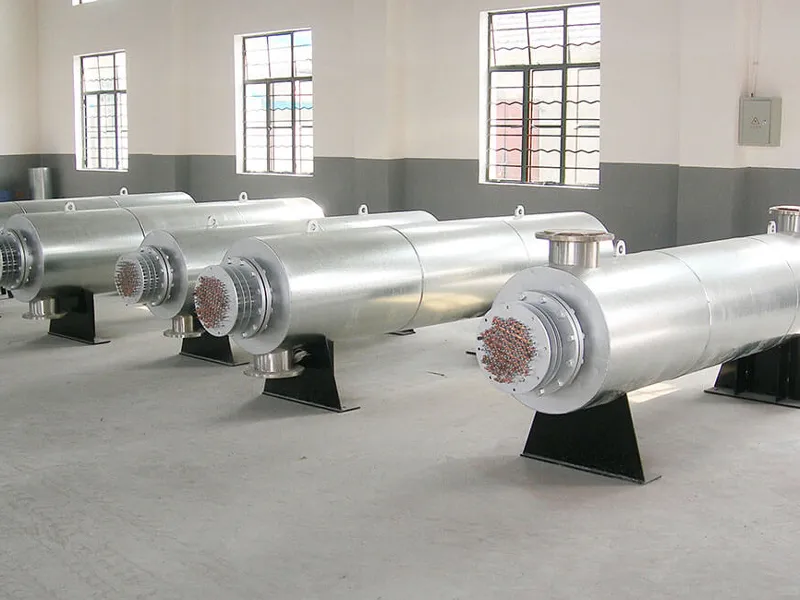
3. Special Materials for Harsh or Sensitive Environments
Standard models often use carbon steel or basic stainless steel construction, suitable for most thermal fluids and environments. However, non-standard applications may demand enhanced material durability, especially when operating in corrosive, high-purity, or explosive environments.
Custom heaters can be built using:
High-alloy steels (e.g., Inconel, Hastelloy) for chemical resistance
316L stainless steel for sanitary or pharmaceutical use
Teflon-coated or ceramic-insulated components for high-purity or cleanroom environments
Weather-resistant or marine-grade enclosures for outdoor or coastal installations
This material flexibility ensures longer lifespan, improved safety, and compatibility with specialized fluids or environmental conditions.
4. Advanced Control and Monitoring Systems
Standard heaters usually include basic thermostats, over-temperature cutoffs, and analog control systems. In contrast, custom heaters often incorporate advanced electronic control systems, tailored to the customer’s process automation setup.
Typical custom control features include:
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) with user-defined logic
Touchscreen Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) for intuitive operation
Remote monitoring and diagnostics via Ethernet, Modbus, or IoT platforms
Multi-loop temperature control for systems with multiple heating zones
Integration with SCADA, DCS, or building automation systems
These advanced systems enhance process reliability, allow for data-driven optimization, and improve fault detection and maintenance planning.
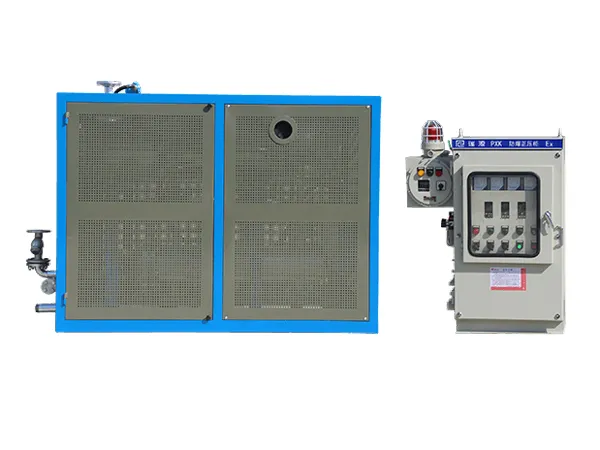
5. Explosion-Proof and Hazardous Area Certification
Many industries—such as oil & gas, chemical processing, and mining—operate in hazardous environments where explosive vapors or dust are present. Standard heaters are not built to handle these risks.
Custom thermal oil heaters can be built to meet:
ATEX / IECEx certification for explosive atmospheres
UL or CSA Class I, Div 1 or Div 2 ratings for North American compliance
Flameproof or intrinsically safe enclosures for electrical components
Purge and pressurization systems to maintain safety in control panels
These safety measures are essential for protecting personnel and equipment in volatile environments.
6. High-Performance Applications
Standard heaters are typically limited to temperature ranges of 300–350°C and flow rates suited for basic heating loops. Custom heaters, however, can be engineered for higher performance:
High temperature operation (above 400°C), with specially designed heating elements and insulation
High fluid velocity or pressure to reduce film temperature and prevent oil degradation
Rapid heat-up cycles for batch or dynamic systems
Multi-zone output to deliver different temperatures to different process lines
These performance enhancements are often necessary for industries like aerospace, plastics processing, and specialty chemicals.
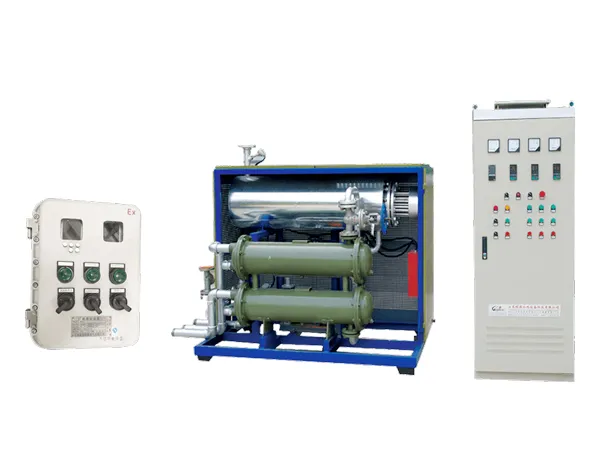
7. Integrated Systems and Modular Design
While standard heaters often operate as stand-alone units, custom thermal oil heaters are frequently integrated into complete heating systems, designed and built by the manufacturer. These modular systems may include:
Circulation pumps (single or redundant)
Expansion tanks and level sensors
Deaeration systems
Bypass valves and pressure regulators
Heat exchangers for secondary loops
Cooling modules for precise temperature control
These systems are often pre-assembled and tested, minimizing onsite installation work and reducing commissioning time.
8. Comprehensive Compliance and Documentation
Industries like pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, and semiconductors demand strict adherence to industry-specific standards and documentation practices. Custom heaters can be built to comply with:
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices)
FDA/NSF material standards
ISO 9001 traceability requirements
ASME design codes for pressure systems
Manufacturers often provide full documentation packages, including:
Material traceability certificates
Welding qualifications
FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) and SAT (Site Acceptance Test) reports
Electrical schematics and PID drawings
This level of compliance is not typically offered with standard models.
9. Cost vs. Value Consideration
Custom thermal oil heaters generally cost more than standard units, both in upfront pricing and lead time. However, the added value lies in performance, efficiency, reliability, and lifecycle savings.
Benefits include:
Fewer shutdowns due to better system integration
Lower maintenance costs thanks to materials suited to the environment
Higher energy efficiency through optimized heating and control systems
Improved safety and regulatory compliance, reducing liability risks
For critical processes or regulated industries, a custom heater often pays for itself many times over.