-
tel:
+86-15371113672 -
WhatsApp:
+86-15371113672 -
email:
qianli@jsryan.com
How Does an Electric Process Air Heater Work?
News List
- Petroleum and Gas
- How Do You Maintain and Service Non-Standard Custom Electric Thermal Oil Heaters?
- Are Electric Process Air Heaters Energy-Efficient?
- What Safety Features Should in a Non-Standard Custom Electric Thermal Oil Heater?
- What Are the Key Advantages of Using Electric Air Heaters Over Traditional Heating Methods?
- What Are the Benefits of Using Thermal Oil as a Heat Transfer Medium?
- How Does an Electric Process Air Heater Work?
- What Makes a Non-Standard Custom Electric Thermal Oil Heater Different from Standard Models?
- What Industries Benefit from Electric Process Air Heaters?
- Client feedback of Vacuum pyrolysis oven and preheat oven
- Suggestions for selecting electric thermal oil heater
- How to install and use the electric thermal oil heater
- Deliver five sets of explosion-proof organic fluid boiler with cool unit
How Does an Electric Process Air Heater Work?
11 Jun
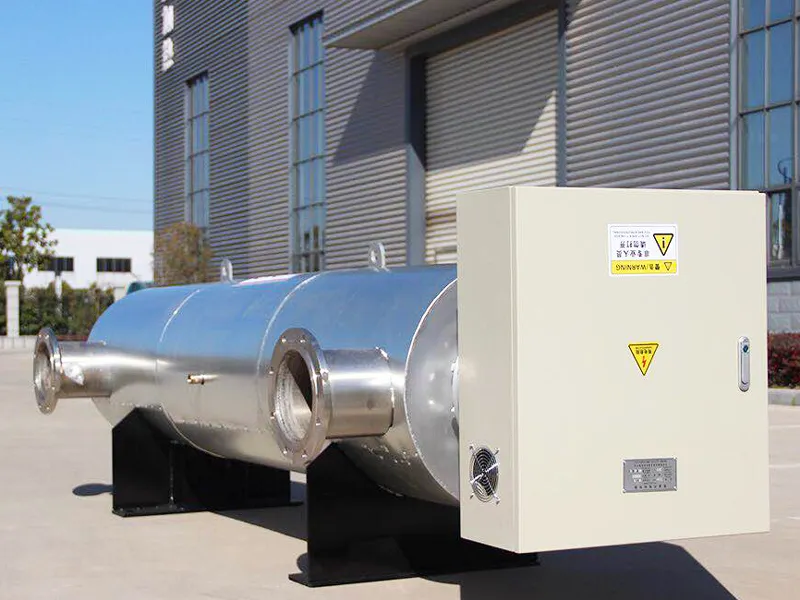
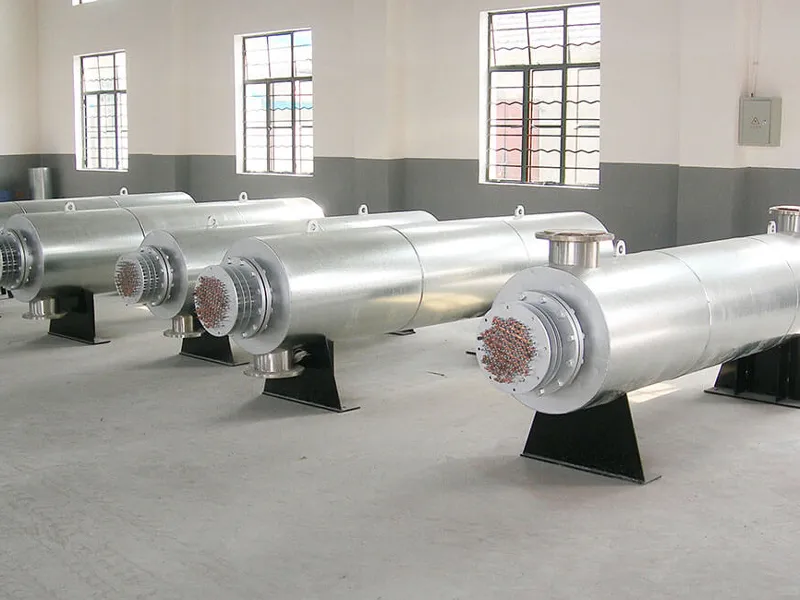
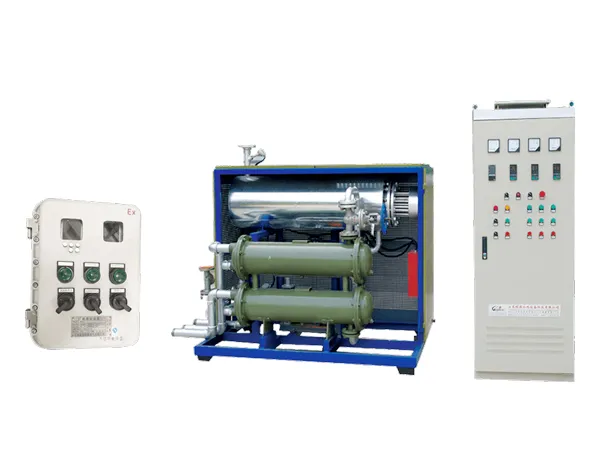
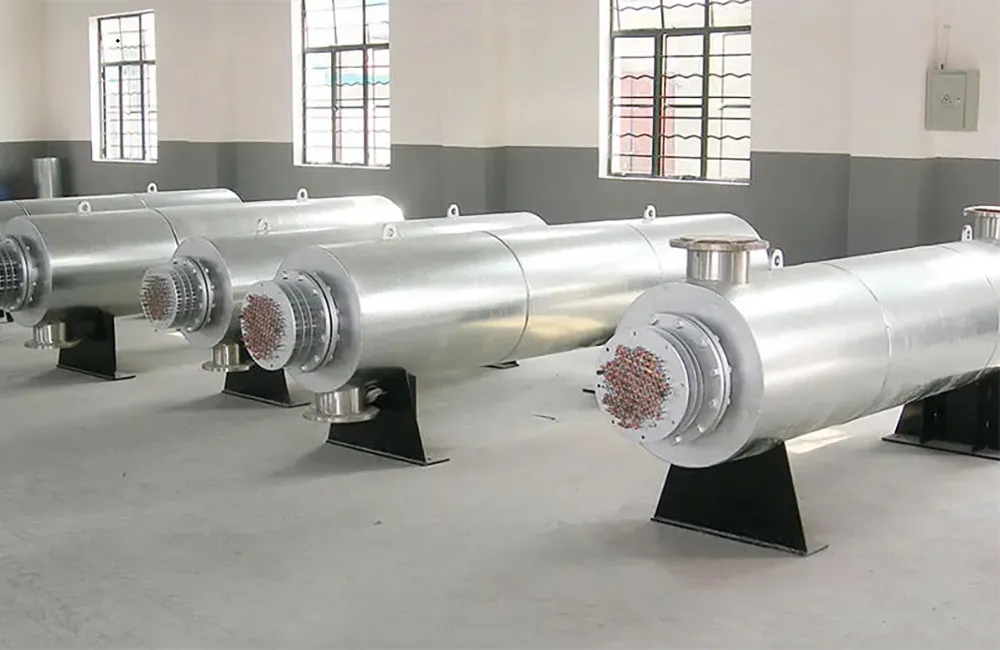
Electric Process Air Heaters are devices designed to heat air for industrial processes. They are commonly used in environments where precise temperature control of the air is critical for efficiency, product quality, or safety.
Basic Working Principle
An electric process air heater functions by using electric heating elements to raise the temperature of the incoming air. The basic components of these heaters include:
Heating Elements: These are typically made of high-resistance materials (such as nichrome) that convert electrical energy into heat. When electricity passes through the heating elements, they heat up and transfer that heat to the air.
Air Flow System: A fan or blower is usually integrated into the system to force air over or through the heating elements. This ensures that the heated air is distributed effectively throughout the system.
Temperature Control: Temperature sensors and thermostats monitor the air's temperature and adjust the power supplied to the heating elements accordingly. This allows the system to maintain a constant temperature, even with fluctuations in ambient conditions or air flow.
Detailed Process
When air enters the heater, it is usually at room temperature or lower, depending on the environment. As it passes through the heating chamber, the air is directed over the electric heating elements, where it is warmed up. The heated air then exits the heater and is directed to the process or space that requires heat.
The primary factors affecting the performance of an electric process air heater are:
Air Flow Rate: The volume of air that passes through the heater determines how much heat can be transferred. Higher air flow rates require more powerful heating elements to maintain the desired temperature.
Heating Element Design: Different designs of heating elements can provide varying amounts of heat per unit of electrical power. Efficient designs improve energy consumption.
Temperature Control: Modern electric air heaters come equipped with sophisticated control systems that automatically adjust the output to keep the air temperature within the specified range. These may include PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers, which optimize temperature accuracy.
Efficiency
Electric process air heaters are highly efficient because they convert nearly all of the electrical energy into heat. Unlike fossil fuel-based systems, they don’t lose energy through combustion, which makes them ideal for applications where precise heating is essential.